



Almost immediately after the Su-7 fighter-bomber was accepted into service in 1959, a directorate was issued to vastly upgrade the aircraft, as technology of the '50s and '60s was rapidly advancing and leaving the Su-7 behind. Throughout the early '60s, many avionics and ordnance upgrades were experimented with, but the largest change would not come from the Soviets, but rather, the Americans. In 1964, the culmination of the USAF's TFX program, the F-111 "Aardvark", performed its first flight, and presented to the world the dynamics of variable-geometry wings. The Soviets, as not to be out-done, hammered a partially variable geometry wing (only the outer half of the wing could pivot) into their updated Su-7 prototype, and redubbed it the Su-17. This new aircraft would first fly only two years later, in 1966, and would enter service as the Su-17M shortly after, with a export variant named the Su-20. The Su-17 and its derivatives would serve a long life with many operators around the world, from the oriental shores of Vietnam to the mountainous reaches of Peru in South America. Throughout its long life, the Su-17 would be upgraded into many variants, starting with the Su-17M2, and eventually evolving into the Su-17M3 and M4, marketed respectively as the Su-22M3 and M4 for export. Even the Russian Federation would continue to use its later variants after the collapse of the USSR, and the Fitter family still finds use with third world countries to this day, even garnering short-lived fame in recent times in 2017 when a Syrian Su-22M4 defeated the latest AIM-9X fired from a USN F/A-18E Super Hornet in a well documented incident resulting in the last aircraft in recent times shot down by the United States.
The Su-17M2 was introduced in Update "Ixwa Strike" as the first aircraft with variable-geometry wing ("swing wing") mechanics in-game. While underwhelming compared to not only its adversaries, but also its own contemporaries in its own tech tree, the aircraft lays the foundation of skill required to operate other, more advanced swing-wing attack aircraft in the Soviet tech tree, such as the later Su-17M4 and the MiG-27s. Being the first supersonic aircraft with laser guided ordnance in the Soviet tech tree, this aircraft builds on doctrine established from both the slower, more cumbersome Su-25s and the fast and hard-hitting Su-7s, making this plane a stepping stone towards the later Soviet supersonic fighter-bombers.
flaps
flaps
flaps
brake
| Belt | Belt filling | Armor penetration (mm) at a distance: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 m | 100 m | 500 m | 1000 m | 1500 m | 2000 m | ||
| HEF-I/AP-T/HEF-I/APHE | 48 | 47 | 40 | 33 | 27 | 22 | |
| APHE/AP-T/HEF-I | 48 | 47 | 40 | 33 | 27 | 22 | |
| APHE/HEF-I/HEF-I/HEFI-T | 37 | 36 | 31 | 25 | 21 | 17 | |
| Name | Weight | Slot | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 × | 570 kg | 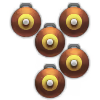 |  | |||||||
| 250 kg |  |  |  |  | ||||||
| 508.3 kg |  |  |  |  | ||||||
| 275 kg |  |  |  |  | ||||||
| 515 kg |  |  |  |  | ||||||
| 374 kg |  |  |  |  | ||||||
| 7 × | 216.5 kg | 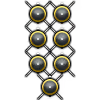 |  |  |  | |||||
| 235 kg |  |  |  |  |  |  | ||||
| 32 × | 225.5 kg |  |  |  |  | |||||
| 20 × | 376 kg |  |  |  |  | |||||
| 318 kg |  |  | ||||||||
| 289 kg |  |  | ||||||||
| Drop tank (820 liters.) | 59.4 kg |  |  |  |  | |||||
| 114 kg |  |  | ||||||||
| 2 × | 87 kg |  |  | |||||||
| 43.5 kg |  |  | ||||||||
| 94.3 kg |  |  | ||||||||
| 4 × | 456 kg |  |  | |||||||
| 3 × | 750 kg |  |  | |||||||
| 2 × | 1,016.6 kg |  |  | |||||||
| 3 × | 825 kg |  |  | |||||||
| 2 × | 1,030 kg |  |  | |||||||
| 657 kg |  | |||||||||
| Projector-1 targeting pod | 20 kg |  |  | |||||||












Flight performance |
|---|
Survivability |
|---|
Weaponry | |||
|---|---|---|---|